MINING BEYOND REALITY
MARVEL TECHNOLOGIES
Introduction
Industry 4.0 is characterized by a combination of cyber-physical systems that uses modern control systems and embedded software systems that is connected using IOT . Mining industries already employ these concepts to look for opportunities and to optimize their processes – embedded sensors, automation, and robotization of production processes. However, the delivery of training and instruction for mining education has largely remained traditional. The necessary skills needed for the mine of tomorrow should be considered. The Industry 4.0 Learning Factory would bridge this gap through a Digital Training Center making use of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR). It envisions an augmented miner with senses and memory extended through technology.
About Marvel
Accelerated R&D Program for Capacity Building of Research and Development Institutions and Industrial Competitiveness: Niche Centers in the Regions for R&D (NICER) Program:Sustainable Mineral and Mining Operations using Industry 4.0
Project Profile
Title: Industry 4.0 Learning Factory for Mining Engineering and Geology in the Academe and Mining Industry using Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) Technologies aka: MARVEL (Mining AR and Virtual ELearning)
Project Leader: Dr. Jaymer M. Jayoma
Cost: PHP10,748,125
Start date: June 1, 2022
End date: December 31, 2024
Implementing Agency: CHCI, CSU, Ampayon, Butuan City
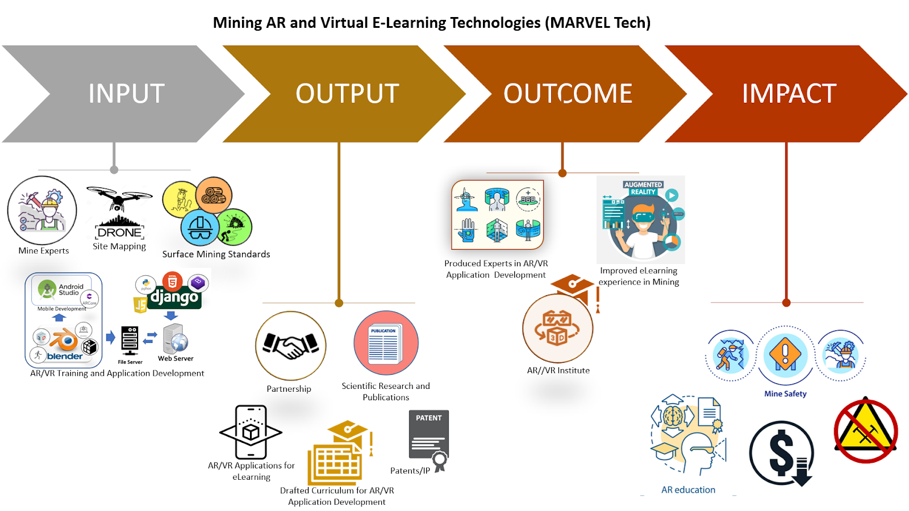
STATEMENT OF OBJECTIVES
The general objective of this project is to develop Augmented or Virtual Reality technologies for Mining Processes that can aid in the simulation and training of mining scenarios. This includes training for high-risk situations, such as simulating equipment and machines. Specifically, this proposed project aims to:
1. Develop AR/VR for Anatomy of a Mine
2. Develop AR/VR for Mine Safety Training and Drills: mine emergency rescue and evacuation; and
3. Develop AR/VR for Mining Machine Operations like Jack Leg Rock Drilling Machine and others
RATIONALE/SIGNIFICANCE
Industry 4.0 is characterized by a combination of cyber-physical systems that uses modern control systems and embedded software systems that is connected using IOT . Mining industries already employ these concepts to look for opportunities and to optimize their processes – embedded sensors, automation, and robotization of production processes. However, the delivery of training and instruction for mining education has largely remained traditional. The necessary skills needed for the mine of tomorrow should be considered. The Industry 4.0 Learning Factory would bridge this gap through a Digital Training Center making use of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR). It envisions an augmented miner with senses and memory extended through technology.
In particular, mine safety involves a broad array of related risks and hazards associated with mining. These include blasting explosives, ergonomics, diesel and dust control, fire and explosion safety, structural safety in mine construction and geologic characterization, and environmental safety.
With these issues, it is imperative to limit or eliminate human activities in the mining sites by implementing Augmented / Virtual Reality (AR/VR) that mimics mining management, especially on safety. AR and VR technologies will enable schools and mining companies to implement laboratory and site management through a simulation that can enable them to save costs with the same efficiency. Equipment only available to the mine site can also be simulated to continue the delivery of necessary coursework even outside the physical classroom or laboratory. This will also ensure continuous delivery of training even during sudden unforeseen events just like the CoViD-19 pandemic.
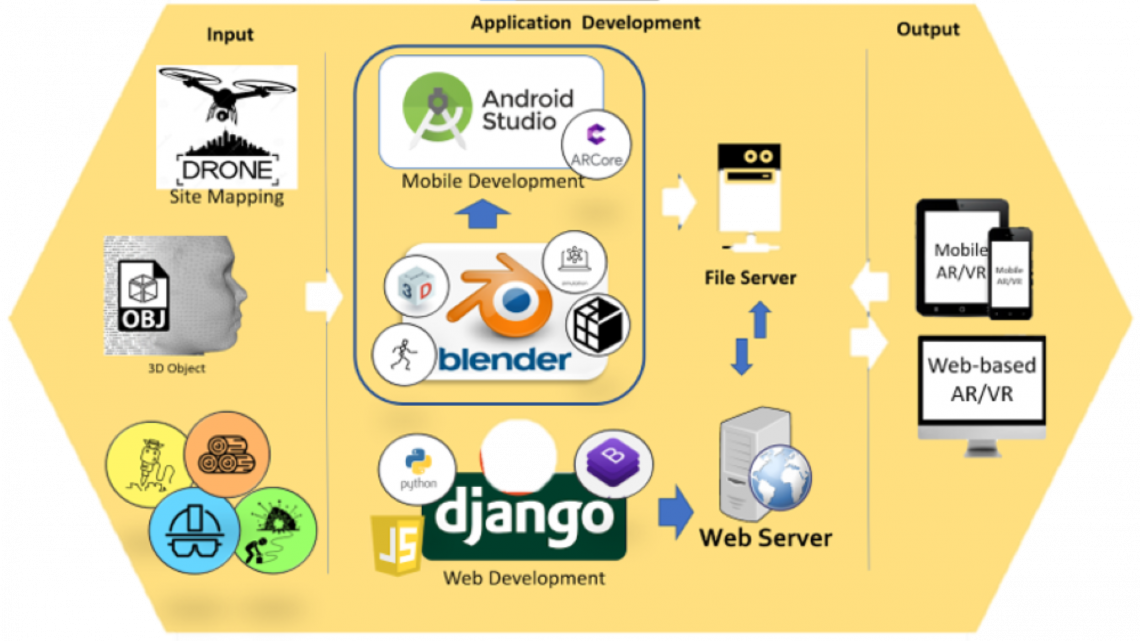
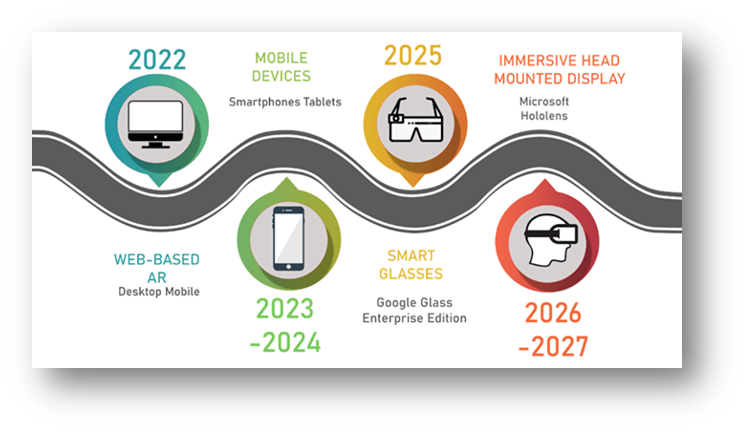
METHODOLOGY
Industry 4.0 is characterized by a combination of cyber-physical systems that uses modern control systems and embedded software systems that is connected using IOT . Mining industries already employ these concepts to look for opportunities and to optimize their processes – embedded sensors, automation, and robotization of production processes. However, the delivery of training and instruction for mining education has largely remained traditional. The necessary skills needed for the mine of tomorrow should be considered. The Industry 4.0 Learning Factory would bridge this gap through a Digital Training Center making use of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR). It envisions an augmented miner with senses and memory extended through technology.
In particular, mine safety involves a broad array of related risks and hazards associated with mining. These include blasting explosives, ergonomics, diesel and dust control, fire and explosion safety, structural safety in mine construction and geologic characterization, and environmental safety.
With these issues, it is imperative to limit or eliminate human activities in the mining sites by implementing Augmented / Virtual Reality (AR/VR) that mimics mining management, especially on safety. AR and VR technologies will enable schools and mining companies to implement laboratory and site management through a simulation that can enable them to save costs with the same efficiency. Equipment only available to the mine site can also be simulated to continue the delivery of necessary coursework even outside the physical classroom or laboratory. This will also ensure continuous delivery of training even during sudden unforeseen events just like the CoViD-19 pandemic.
FEATURED OUTPUT
AUGMENTED REALITY
Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that blends digital elements with the real world, allowing users to experience enhanced environments through devices like smartphones, tablets, or specialized AR glasses. Unlike Virtual Reality (VR), which immerses users in entirely digital worlds, AR overlays digital content—such as images, sounds, or 3D models—onto the physical environment in real time. This allows users to interact with both virtual and real objects simultaneously.
Popular examples of AR include games like Pokémon Go, where virtual creatures appear in real-world locations, and navigation tools like Google Maps AR, which projects directions onto the streets as you walk. In retail, AR apps help customers visualize how furniture, clothing, or makeup might look in their own space or on themselves before making a purchase. The technology has applications in various fields, including entertainment, education, healthcare, and marketing, offering immersive, interactive experiences that enhance how people perceive and interact with the world around them.
OUR TEAM




Contact Us
We interact in the modern world.
Learn More From
Frequently Asked Questions
It is located at the 2nd floor, Hiraya Building, Caraga State University
The Center for Human-Computer Interaction(CHCI) at Caraga State University is a University wide research center that addresses the foundation of human computer interaction technology applied to learning environments, social and rural contexts. It is a multidisciplinary endeavor from human sciences, computational, engineering and information technologies.
It fosters research and development in the area of artificial intelligence, augmented reality and other HCIs related fields of organization.
CHCI was founded in 2018.
Mining Augmented Reality and Virtual E-Learning Technologies.
The Farm-to-Market Road Impact Assessment (FaMRIA) Project is a collaboration between Caraga State University (CSU) and the Department of Agriculture- Bureau of Agricultural and Fisheries Engineering (DA-BAFE).